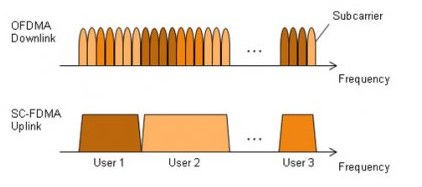
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution. It is the technology that superseded GSM (2G), and UMTS (3G) as a packet switched network. The multiple access technique utilized is OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex) in the downlink and SC-FDMA (Single Carrier - Frequency Division Multiple Access) in the uplink. This modulation technique allows for many subcarriers to be close together, hence making the system robust to interference as well as improving spectral efficiency. As a result, more data can be sent in the same frequency bandwidth - which also translates to faster data rates.
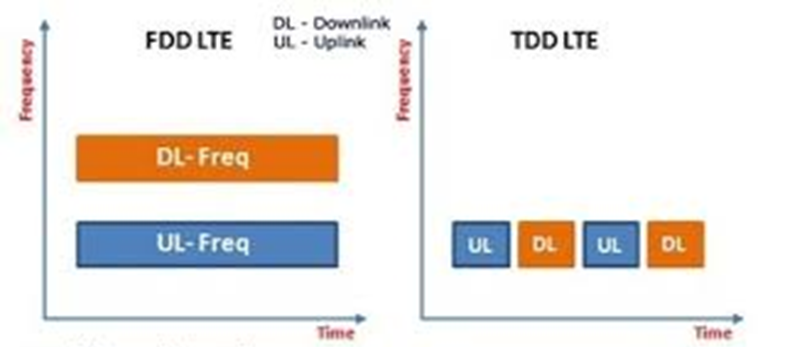
There are two ways in which LTE can operate. It can operate in either the frequency or time domain as FDD and TDD.
•LTE FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) requires two separate wireless communication channels on separate frequencies, one for transmit and the other for received data
•LTE TDD (Time Division Duplex) TDD uses a single frequency band for both transmit and receive. Then it shares that band by assigning alternating time slots to transmit and receive operations
The diagram below helps illustrate the differences.
LTE PARAMETERS
RSRP indicates signal strength and is the average power received from a single reference signal (one resource element). It is used for cell selection, cell reselection, power control calculations, mobility procedures and beam management.
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Duplexing | FDD, TDD, Half duplex FDD |
Channel Coding | Turbo Code |